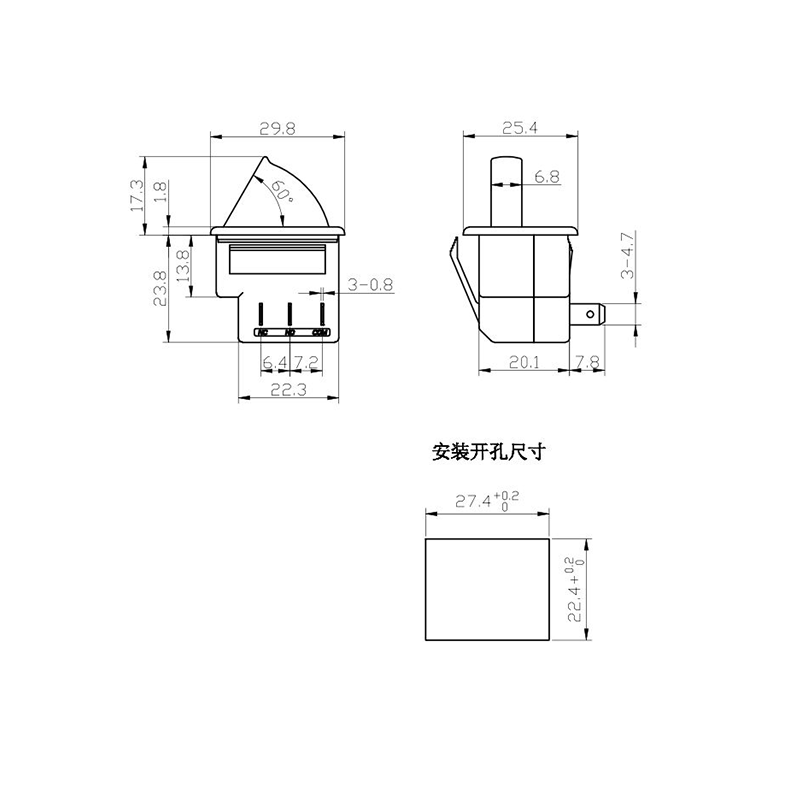
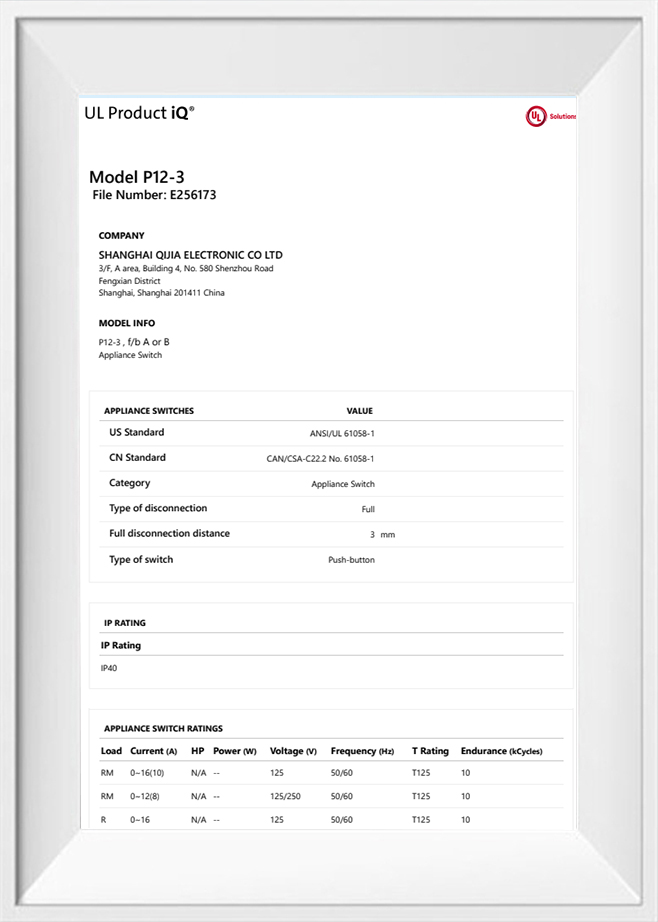
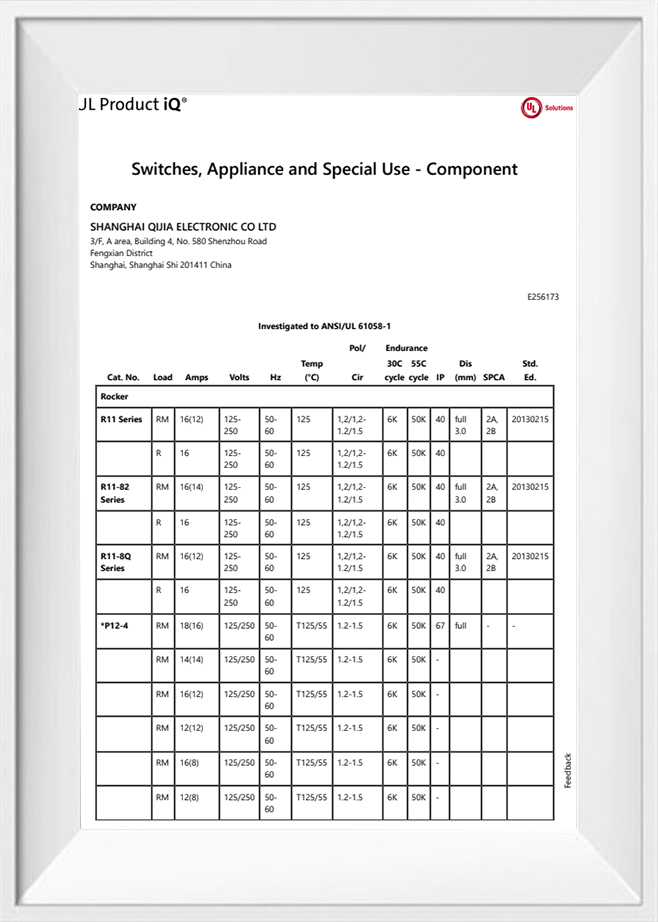
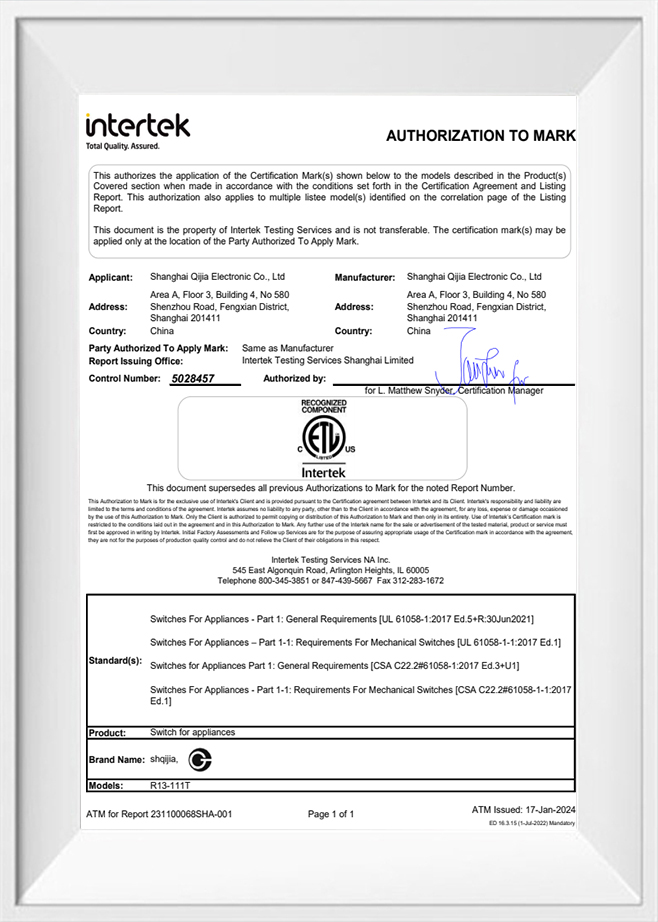
-
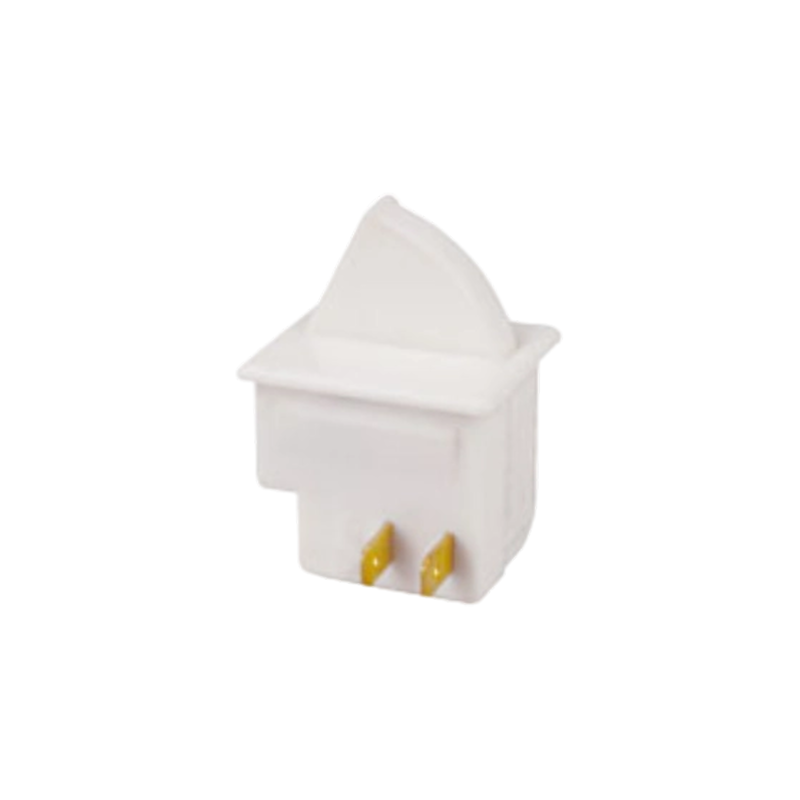
A Rocker Switch is a compact and easy-to-operate manual control component. Its unique rocker-style actuation, combined with a toggle or momentary reset function, allows users to quickly switch circuit...View More >>
-
A micro switch is a small mechanical switch with a fast action mechanism, which is widely used in household appliances, industrial automation, automotive electronics, medical equipment, and other fiel...View More >>
-
Push button switches are widely used in various control systems with their diverse structural designs, high-strength material selection, and excellent performance. The products are available in a vari...View More >>
-
The internal structure of the piano key switch mostly adopts a mechanical or light-touch design. Some high-end models use capacitive sensing technology to achieve contactless operation, thereby improv...View More >>
-
The baby stroller gear switch is an innovative product independently developed by our company. We have applied for invention patents both domestically and internationally, which fully demonstrates the...View More >>
-
The knob switch adopts a high-sensitivity rotary contact structure, which has smooth operation and clear positioning, ensuring that every adjustment is accurate. The product has excellent durability a...View More >>
-
The KM trigger switch is a universal high-current switch designed for high-power power tools, with excellent current carrying capacity and stable performance. The internal fast-action structure ensure...View More >>
-
A door control switch, also known as a door magnetic switch or door status sensor, is a key electrical component widely used in industrial control, security systems, intelligent building automation, a...View More >>
-
The wiring harness is an overall wiring assembly that integrates multiple wires, cables, terminals, and connectors according to specific electrical design and mechanical structure requirements. It is ...View More >>
-
PCB control board is one of the indispensable core components in modern electronic devices. As the brain of the control system, it is widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, consumer...View More >>
Door Control Switches Manufacturers
A door control switch, also known as a door magnetic switch or door status sensor, is a key electrical component widely used in industrial control, security systems, intelligent building automation, and transportation. It is mainly used to detect the open and closed state of the door and convert the information into electrical signal output to achieve linkage control of access control, lighting, ventilation, alarm, and other systems. The door control switch is usually composed of a magnet component and induction component and triggers the internal circuit to open and close through the change of magnetic field. Common types include dry contact door magnetic switch, Hall effect sensor type, photoelectric door control switch, and wireless door control sensor.
About SHQIJIA
Shanghai Qijia Electronics Co., Ltd. was founded in 2004. After more than two decades of development and accumulation, it has grown into a high-tech enterprise integrating the design, R&D, manufacturing, sales, and service of high-quality appliance switches, as Door Control Switches Manufacturers and Door Control Switches Factory in China, we establish a professional and reliable brand image in the industry.
The company's core product line, "shqijia," covers a wide range of AC and DC appliance switches, including micro switches, rocker switches, pushbutton switches, trigger switches, and rotary switches, as well as AC and DC circuit board modules and controllers. These products are widely used in AC and DC power tools, electric garden tools, cleaning equipment, household appliances, medical equipment (oxygen concentrators), generators, electric strollers, water pumps, and other electronic and mechanical fields, providing customers in various industries with highly adaptable core component solutions.
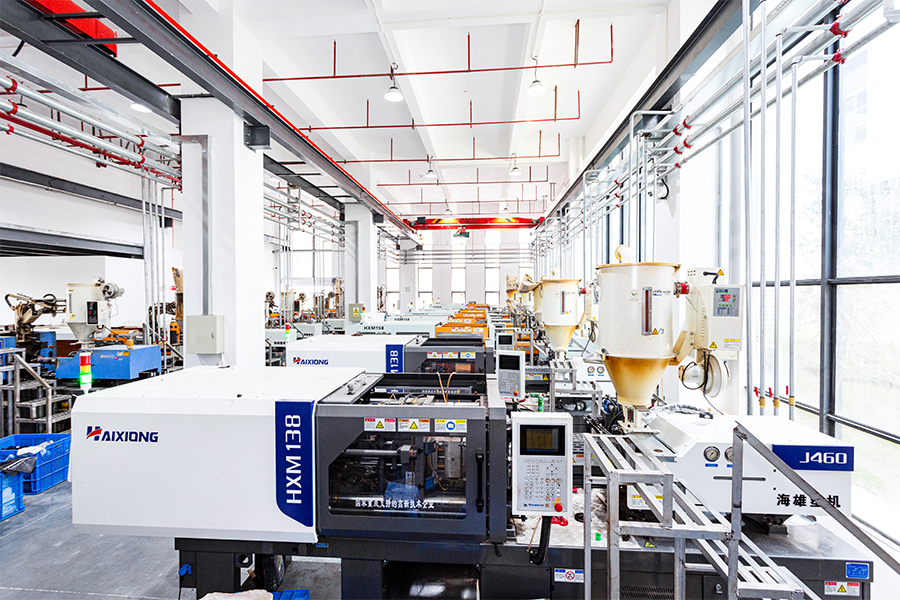
In 2025, the company opened a new factory Withover 20 assembly lines, more than 20 injection molding machines, and over 40 automated equipment, the company boasts an annual production capacity exceeding 80 million units, providing stable and efficient product supply support to customers worldwide. In addition, we support Door Control Switches Custom, the company possesses professional independent product and mold design capabilities, providing customized development services based on individual customer needs and precisely matching diverse application scenarios.
With superior quality, advanced manufacturing processes, competitive pricing, and comprehensive after-sales service, Qijia has earned widespread recognition and trust from customers worldwide.

Certificate
Latest Updates
Industry knowledge
Door Control Switches: The Silent Guardians of Modern Access
Door Control Switches are specialized electromechanical devices forming the fundamental layer of security and automation in commercial, industrial, and residential settings. Far from being simple on/off buttons, these components are highly engineered sensors and interfaces that determine the operational state and security integrity of any controlled opening.
I. The Core Functionality: Categories and Technology
Door control switches are defined by their application, primarily falling into three technical categories:
1. Door Position Monitoring (DPS)
The primary role of the DPS is to report the real-time physical status of the door to a central control unit (like an alarm panel or access controller).
-
Magnetic Reed Switches: These non-contact sensors are the most common DPS. They consist of a permanent magnet (on the door) and a sealed reed switch (in the frame). The presence or absence of the magnetic field changes the switch's contact state (Normally Open/Normally Closed), signaling an intrusion or confirming closure.
-
Mechanical Limit Switches: These switches require physical contact with the door leaf to actuate. They are often used when higher reliability under specific environmental conditions is required, such as in heavy-duty machinery gates or industrial environments.
2. Request-to-Exit (RTE) Switches
RTE devices provide a legal and immediate means for occupants inside a secured area to exit, bypassing the access credentials (key card, code) required for entry.
-
Touchless/Non-Contact Switches: Utilizing IR or microwave sensing, these devices actuate when a hand is waved nearby. This technology is becoming the standard in hygienic environments (hospitals, food prep areas) to prevent cross-contamination.
-
Push Plate/Jumbo Push Buttons: These large, highly visible mechanical switches are designed for easy activation, often meeting ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) requirements.
3. Operational Mode Selectors
These switches are critical in automated door systems (sliding, revolving, folding) to define the door’s behavior based on facility needs or time of day.
-
Multi-Position Key Switches/Rotary Selectors: These allow authorized personnel to manually switch between modes such as:
-
Automatic (Auto): Normal sensor-activated operation.
-
Hold Open: Door remains fully open for high traffic or loading.
-
Night/Lock: Door is disabled and secured.
-
Partial/Winter Mode: Door opens only to a limited width for energy saving.
-
II. Essential Technical Requirements and Compliance
The performance of door control switches is governed by strict technical specifications and international compliance standards:
-
Contact Ratings: The switch must be rated to handle the electrical load, especially when controlling high-power devices like magnetic locks or electric strikes. Reliability hinges on matching the switch's Rated Voltage and Current.
-
Durability and Cycle Life: RTE switches, in particular, must exhibit high mechanical endurance, often rated for hundreds of thousands of cycles to withstand constant use in commercial settings.
-
Environmental Protection (IP Rating): Switches used on exterior doors or in wet industrial areas require higher ingress protection (IP) ratings to resist dust and moisture penetration.
-
Certifications: Compliance with certifications like UL, CE, and TÜV is non-negotiable, ensuring the product meets safety and performance standards required for integration into commercial building systems globally.
III. The Foundation of Control: A Specialized Manufacturing Base
The reliability of specialized door control switches and the broader category of appliance and industrial switches relies on a strong foundation of manufacturing expertise.
Shanghai Qijia Electronics Co., Ltd., a high-tech enterprise established in 2004, represents this commitment to quality. While primarily known for its extensive range of high-quality appliance switches—including micro switches, rocker switches, and pushbuttons—used across industries from power tools to medical equipment, its core competency in electromechanical design, automated manufacturing, and rigorous testing standards (compliant with ISO 9001 and accredited by the US UL WTDP Witnessed Laboratory) provides the backbone for reliable control solutions across diverse application scenarios, reinforcing the quality chain for critical components globally.





 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español  Deutsch
Deutsch  عربى
عربى